Analyze RNAseq with DESeq2
2022, Aug 03
Introduction
Here we try to use data from SRA project code SRP029880 and analyze to the fullest.
The tutorial is exactly same in CompGenomicR book
Load data
#colorectal cancer
counts_file <- "SRP029880.raw_counts.tsv"
coldata_file <- "SRP029880.colData.tsv"
counts <- as.matrix(read.table(counts_file, header = T, sep = '\t'))
colData <- read.table(coldata_file, header = T, sep = '\t',
stringsAsFactors = TRUE)
Look into summary
summary(counts[,1:3])
CASE_1 CASE_2 CASE_3
Min. : 0 Min. : 0 Min. : 0
1st Qu.: 5155 1st Qu.: 6464 1st Qu.: 3972
Median : 80023 Median : 85064 Median : 64145
Mean : 295932 Mean : 273099 Mean : 263045
3rd Qu.: 252164 3rd Qu.: 245484 3rd Qu.: 210788
Max. :205067466 Max. :105248041 Max. :222511278
calculate TPM
# create a vector of gene lengths
geneLengths <- as.vector(subset(counts, select = c(width)))
#find gene length normalized values
rpk <- apply( subset(counts, select = c(-width)), 2,
function(x) x/(geneLengths/1000))
#normalize by the sample size using rpk values
tpm <- apply(rpk, 2, function(x) x / sum(as.numeric(x)) * 10^6)
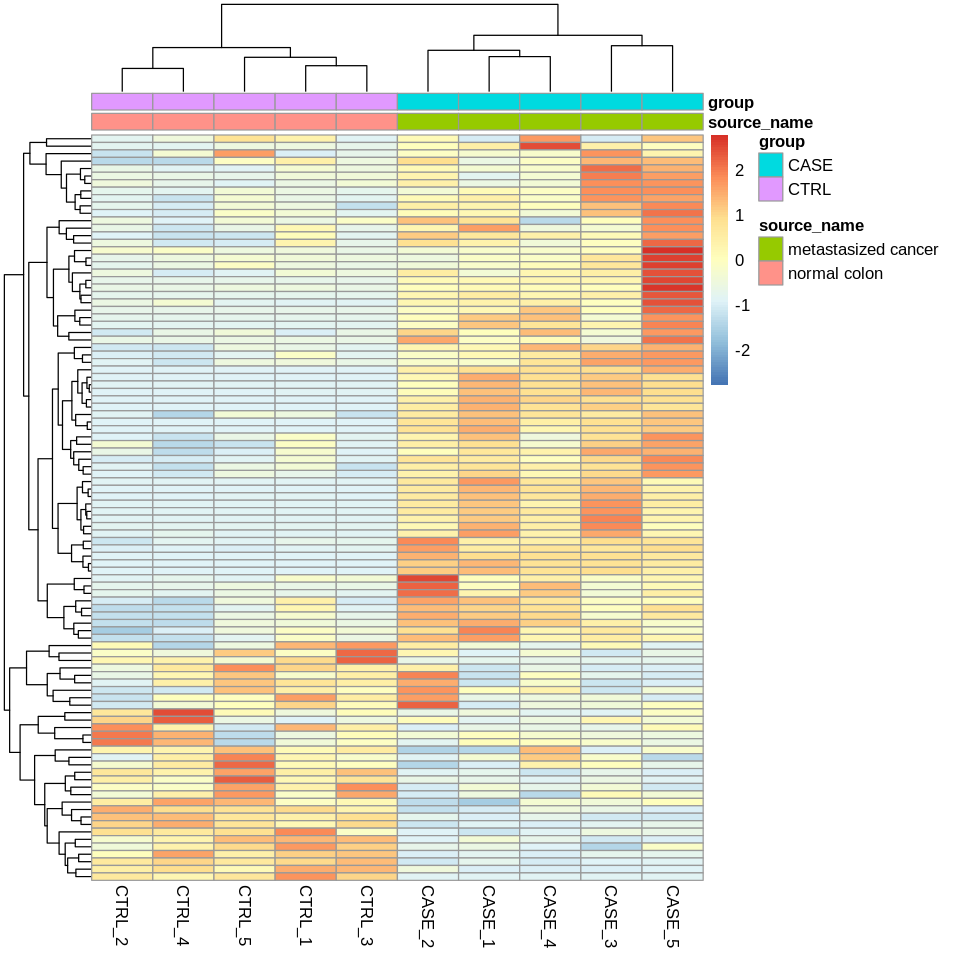
Perform clustering
Perform Clustering with TPM values for quality check:
- Let’s select the top 100 most variable genes among the samples.
- compute the variance of each gene across samples
V <- apply(tpm, 1, var)
#sort the results by variance in decreasing order
#and select the top 100 genes
selectedGenes <- names(V[order(V, decreasing = T)][1:100])
suppressMessages(library(pheatmap))
options(repr.plot.width=8, repr.plot.height=8)
pheatmap(tpm[selectedGenes,], scale = 'row',
show_rownames = FALSE,
annotation_col = colData)
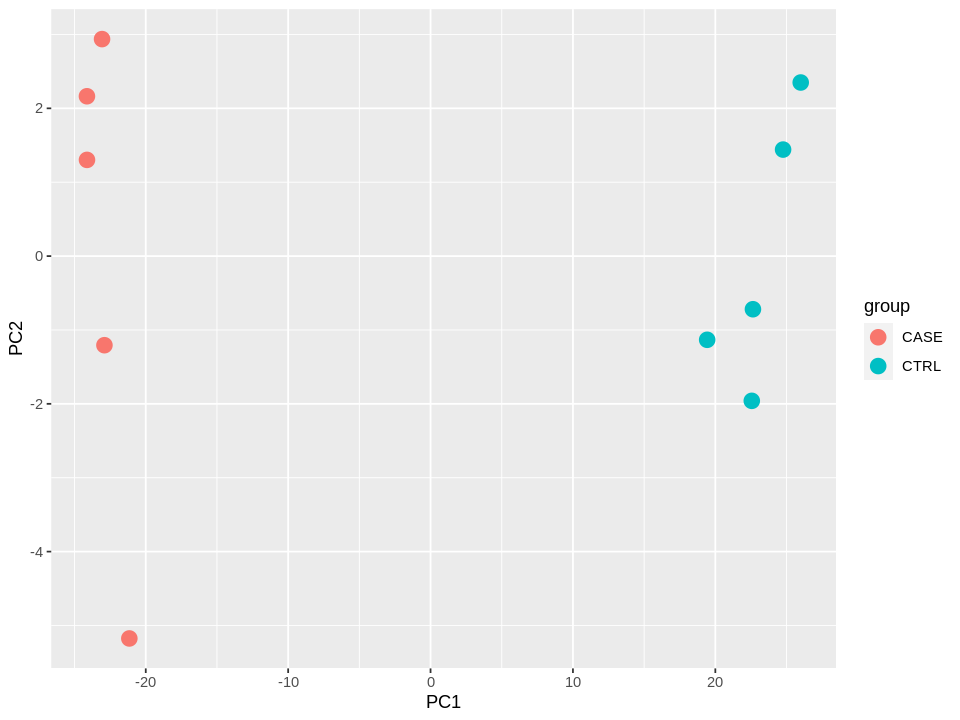
Perform PCA
suppressMessages(library(stats))
suppressMessages(library(ggplot2))
#transpose the matrix
M <- t(tpm[selectedGenes,])
# transform the counts to log2 scale
M <- log2(M + 1)
#compute PCA
pcaResults <- prcomp(M)
#plot PCA results making use of ggplot2's autoplot function
#ggfortify is needed to let ggplot2 know about PCA data structure.
# autoplot(pcaResults, data = colData, colour = 'group')
options(repr.plot.width=8, repr.plot.height=6)
dtp <- data.frame('group' = colData$group, pcaResults$x[,1:2]) # the first two componets are selected (NB: you can also select 3 for 3D plottings or 3+)
ggplot(data = dtp) +
geom_point(aes(x = PC1,
y = PC2,
col = group),
size=4
)
summary(pcaResults)
Importance of components:
PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 PC6 PC7
Standard deviation 24.396 2.50514 2.39327 1.93841 1.79193 1.6357 1.46059
Proportion of Variance 0.957 0.01009 0.00921 0.00604 0.00516 0.0043 0.00343
Cumulative Proportion 0.957 0.96706 0.97627 0.98231 0.98747 0.9918 0.99520
PC8 PC9 PC10
Standard deviation 1.30902 1.12657 4.362e-15
Proportion of Variance 0.00276 0.00204 0.000e+00
Cumulative Proportion 0.99796 1.00000 1.000e+00
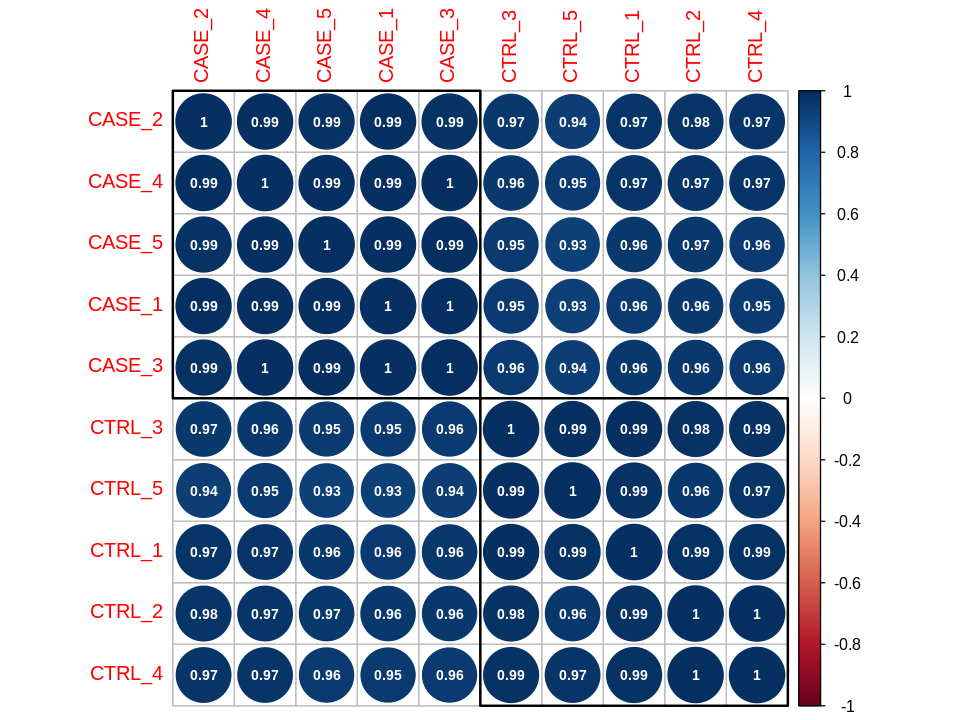
Correlation plots
suppressMessages(library(stats))
correlationMatrix <- cor(tpm)
suppressMessages(library(corrplot))
corrplot(correlationMatrix, order = 'hclust',
addrect = 2, addCoef.col = 'white',
number.cex = 0.7)
options(repr.plot.width=8, repr.plot.height=5)
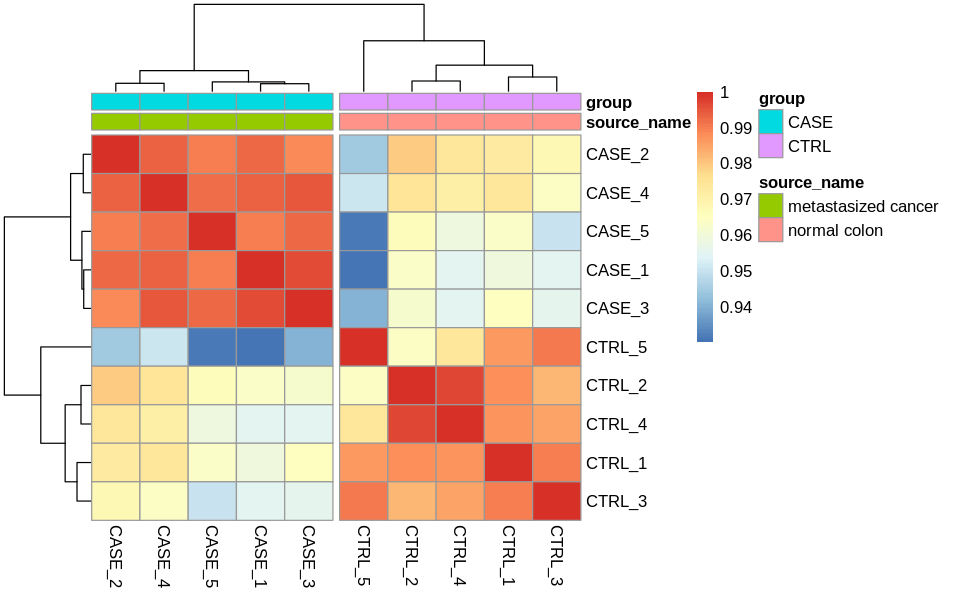
# split the clusters into two based on the clustering similarity
pheatmap(correlationMatrix,
annotation_col = colData,
cutree_cols = 2)
Differential expression analysis
With DESeq2
suppressMessages(library(DESeq2))
#remove the 'width' column
countData <- as.matrix(subset(counts, select = c(-width)))
#define the experimental setup
colData <- read.table(coldata_file, header = T, sep = '\t',
stringsAsFactors = TRUE)
#define the design formula
designFormula <- "~ group"
create a DESeq dataset object from the count matrix and the colData
dds <- DESeqDataSetFromMatrix(countData = countData,
colData = colData,
design = as.formula(designFormula))
#print dds object to see the contents
print(dds)
converting counts to integer mode
class: DESeqDataSet
dim: 19719 10
metadata(1): version
assays(1): counts
rownames(19719): TSPAN6 TNMD ... MYOCOS HSFX3
rowData names(0):
colnames(10): CASE_1 CASE_2 ... CTRL_4 CTRL_5
colData names(2): source_name group
Remove genes that have almost no information in any of the given samples.
#For each gene, we count the total number of reads for that gene in all samples
#and remove those that don't have at least 1 read.
dds <- dds[ rowSums(DESeq2::counts(dds)) > 1, ]
dds <- DESeq(dds)
estimating size factors
estimating dispersions
gene-wise dispersion estimates
mean-dispersion relationship
final dispersion estimates
fitting model and testing
Now, we can compare and contrast the samples based on different variables of interest. In this case, we currently have only one variable, which is the group variable that determines if a sample belongs to the CASE group or the CTRL group.
#compute the contrast for the 'group' variable where 'CTRL'
#samples are used as the control group.
DEresults = results(dds, contrast = c("group", 'CASE', 'CTRL'))
#sort results by increasing p-value
DEresults <- DEresults[order(DEresults$pvalue),]
Let’s have a look at the contents of the DEresults table.
#shows a summary of the results
print(DEresults)
log2 fold change (MLE): group CASE vs CTRL
Wald test p-value: group CASE vs CTRL
DataFrame with 19097 rows and 6 columns
baseMean log2FoldChange lfcSE stat pvalue
<numeric> <numeric> <numeric> <numeric> <numeric>
CYP2E1 4829889 9.36024 0.215223 43.4909 0.00000e+00
FCGBP 10349993 -7.57579 0.186433 -40.6355 0.00000e+00
ASGR2 426422 8.01830 0.216207 37.0863 4.67898e-301
GCKR 100183 7.82841 0.233376 33.5442 1.09479e-246
APOA5 438054 10.20248 0.312500 32.6479 8.58227e-234
... ... ... ... ... ...
CCDC195 20.4981 -0.215607 2.89255 -0.0745386 NA
SPEM3 23.6370 -22.154752 3.02785 -7.3169986 NA
AC022167.5 21.8451 -2.056240 2.89545 -0.7101618 NA
BX276092.9 29.9636 0.407326 2.89048 0.1409199 NA
ETDC 22.5675 -1.795274 2.89421 -0.6202983 NA
padj
<numeric>
CYP2E1 0.00000e+00
FCGBP 0.00000e+00
ASGR2 2.87741e-297
GCKR 5.04945e-243
APOA5 3.16669e-230
... ...
CCDC195 NA
SPEM3 NA
AC022167.5 NA
BX276092.9 NA
ETDC NA
Diagnostic plots
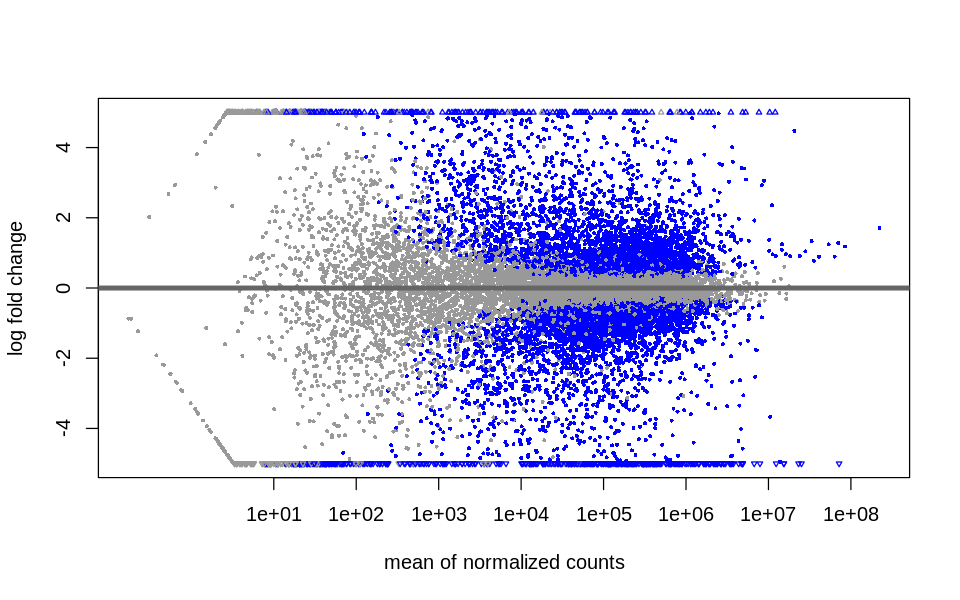
MA plot
DESeq2::plotMA(object = dds,
ylim = c(-5, 5),
# colNonSig = "gray60",
# colSig = "cyan"4
)
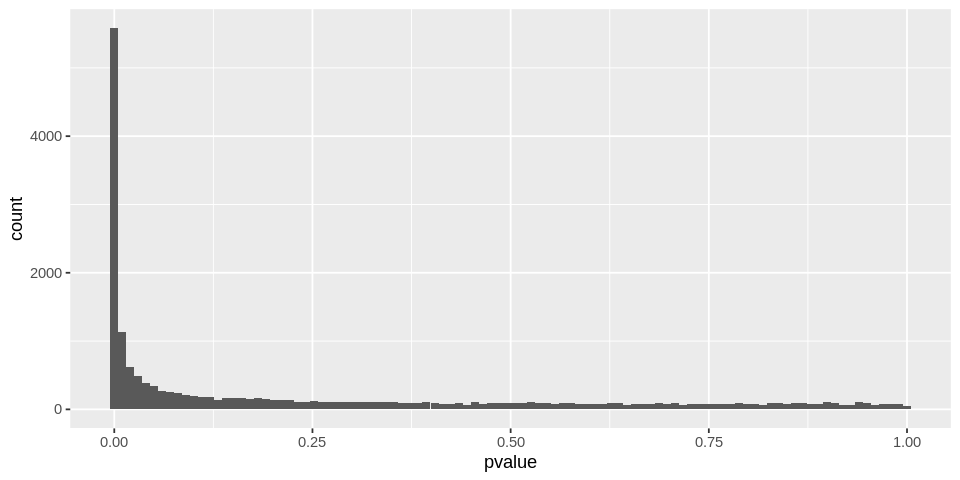
P-value distribution
options(repr.plot.width=8, repr.plot.height=4)
ggplot(data = as.data.frame(DEresults), aes(x = pvalue)) +
geom_histogram(bins = 100)
Warning message:
“Removed 648 rows containing non-finite values (stat_bin).”
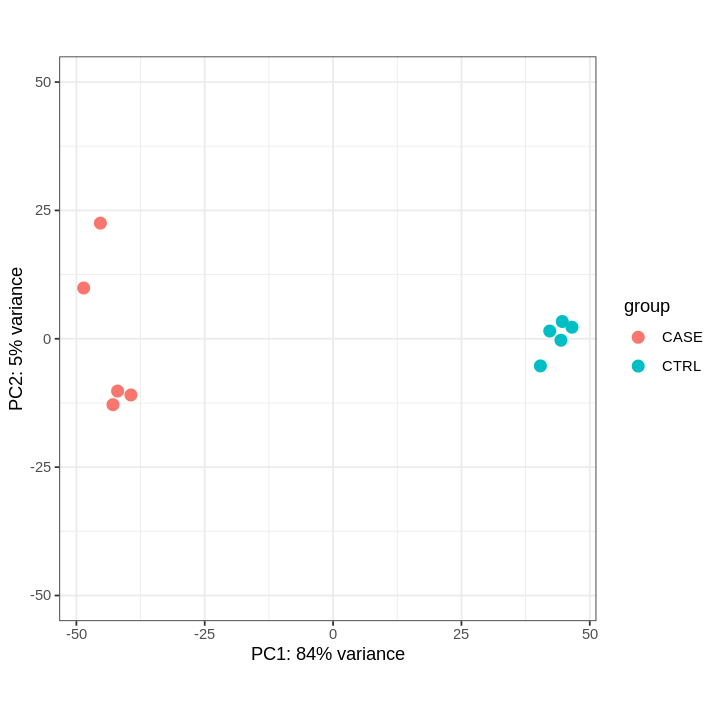
PCA-plot after DESeq2 normalization
# extract normalized counts from the DESeqDataSet object
countsNormalized <- DESeq2::counts(dds, normalized = TRUE)
# select top 500 most variable genes
selectedGenes <- names(sort(apply(countsNormalized, 1, var),
decreasing = TRUE)[1:500])
# NOT WORKING
# plotPCA(countsNormalized[selectedGenes,],
# col = as.numeric(colData$group), adj = 0.5,
# xlim = c(-0.5, 0.5), ylim = c(-0.5, 0.6))
options(repr.plot.width=6, repr.plot.height=6)
rld <- rlog(dds)
DESeq2::plotPCA(rld,
ntop = 500,
intgroup = 'group') +
ylim(-50, 50) +
theme_bw()
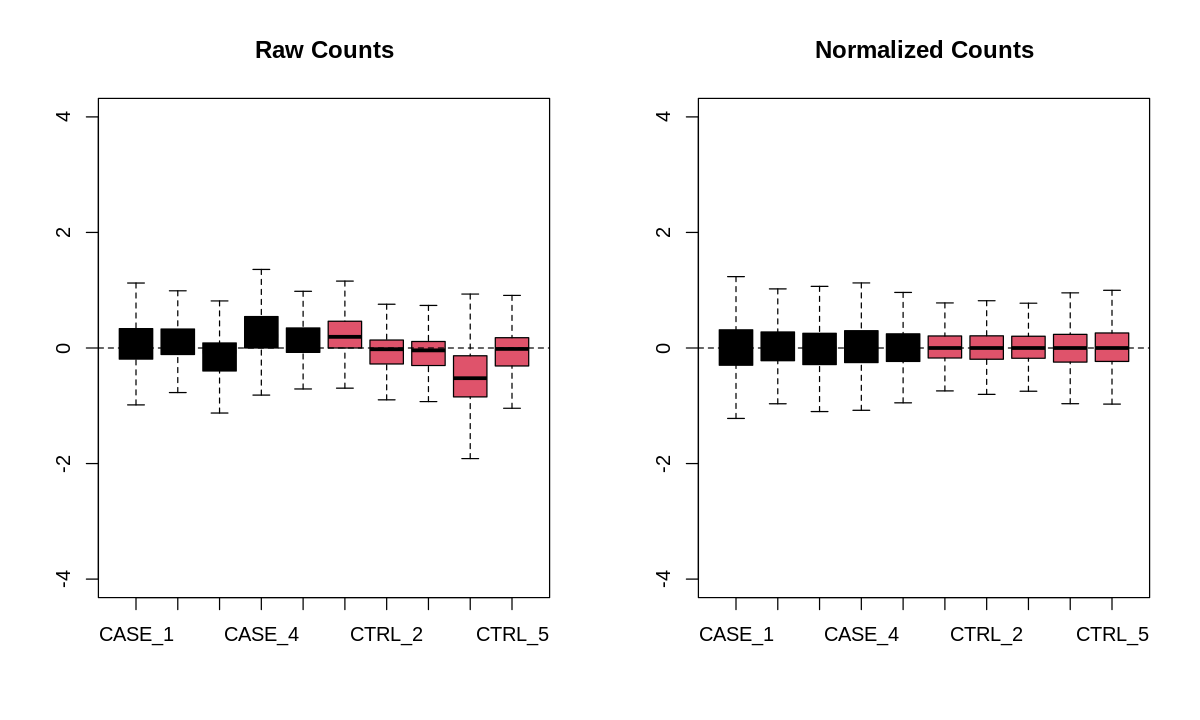
Relative Log Expression (RLE) plot
suppressMessages(library(EDASeq))
options(repr.plot.width=10, repr.plot.height=6)
par(mfrow = c(1, 2))
plotRLE(countData, outline=FALSE, ylim=c(-4, 4),
col=as.numeric(colData$group),
main = 'Raw Counts')
plotRLE(DESeq2::counts(dds, normalized = TRUE),
outline=FALSE, ylim=c(-4, 4),
col = as.numeric(colData$group),
main = 'Normalized Counts')

Functional enrichment analysis
wait for more…